- ABOUT US
- INVESTMENT FUND
- PARTNERSHIP SERVICES
- IMPACT INITIATIVES
-
SPACES
- HONG KONG
- Co-working space
- Event Space
- Prototyping Lab
- LONDON
- Co-working space
- Event Space
-
FABRICA X
- HONG KONG
- Campaign
- Events
- Online Store
- LONDON
- Exhibition
- Retail
- Subscribe
Executive Summary - The Mills Fabrica 2022 Impact Report
We are proud to present the inaugural Impact Report, which showcases our commitment to fostering ecological and social resilience through innovative technologies.
We are excited to present our impact strategy, ethos, and ecosystem of game-changing innovations in the techstyle and agrifood industries.
Our mission has always been to support companies that have the potential to make a positive impact on our planet, and we are thrilled to highlight the incredible achievements of our portfolio companies in this report.
We firmly believe that innovations will play a critical role in driving positive change, and we hope this report serves as a testament to the power of innovations to create a sustainable future.
Download Full Report
- Introduction
- Part 1: Impact Strategy -Planet - Positive Impact Informed by Planetary Thinking
- Part 2: Strategy to Execution - Putting Planetary Thinking into Impact Measurements
- Part 3: Ecosystem of Innovations - Supporting Innovations that are Building Ecological and Social Resilience
- Part 4: Impact Experienced – How our Portfolio Companies are Making Planet-Positive Impact
- Part 5: Portfolio Highlights
Introduction
Climate Change, Ecological Breakdown: it’s apparent more needs to be done.
Our reliance on natural resources for the production of basic necessities such as fibers and food has put our social-ecological system in a perilous position. We are teetering on the edge of a tipping point, and the consequences of inaction could be catastrophic.
It is imperative that we act now and push for innovative solutions to build our social-ecological resilience, as we stand at the brink of a climate catastrophe.
The Mills Fabrica believes innovation in both the techstyle (intersection of technology and lifestyle) and agrifood will be the fundamental catalyst towards ecological and social resilience.
Part 1: Impact Strategy - Planet-Positive Impact Informed by Planetary Thinking
Planetary Awareness: The planetary boundaries framework
The planetary boundaries were developed by the Stockholm Resilience Center to show that nine planetary boundaries maintain the current stable living condition that allows civilization to thrive. Six of the nine planetary boundaries have crossed beyond the safe operating space — including freshwater use, climate change, biosphere integrity, land-system change, novel entities, and biochemical flows.
Essentially, this means humanity is pushing the Earth's natural systems beyond their safe operating limits, potentially leading to irreversible and catastrophic environmental changes.
Textile and apparel, and agrifood industries’ pushing boundaries beyond the safe operating space
The textile and apparel, and agrifood industries combined emit up to 44% of global greenhouse gas emissions —where the textile and apparel industry is estimated to emit up to 10%, and the agrifood industry emits between 26% to 34% of total global emissions — it makes these two industries one of the most significant contributors to climate change.
Apart from greenhouse gas emissions, the textile and apparel, and agrifood industries contribute to the following environmental problems:
- Chemical pollution and excessive use of fertilizers (phosphorus and nitrogen)
- Freshwater use in the cultivation of cash crops (such as cotton), food crops, and throughout both industries’ value chains.
- Land-system change by converting forests, wetlands, grasslands, and other vegetation types into agricultural uses.
- Biodiversity loss from habitat destruction associated with land-system change.
- Release of novel entities such as pesticides, antibiotics, micro/nano plastics.
All these environmental issues can lead to a systemic ecosystem change that reduces society’s resilience to climate change.
Part 2: Strategy to Execution - Putting Planetary Thinking into Impact Measurements
The Mills Fabrica’s Impact Ethos: Planetary Thinking Incorporated
By incorporating planetary thinking into our impact ethos, the key impact themes and metrics we consider when evaluating the impact potential of companies are:
- Greenhouse gas emissions (GHGs) avoided
- Water use reduction
- Land use change avoided
- Eutrophication avoided
- Microplastic and chemicals avoided.
Social impact is based on the IRIS+ framework — the generally accepted system to measure, manage and optimize social and environmental impact measurement used globally by impact investors alike — which will be tailored to each specific investment, though the measurement will revolve around the themes of:
- better health
- wellness
- increased sustainability knowledge
Part 3: Ecosystem of Innovations - Supporting Innovations that are Building Ecological and Social Resilience
Planet-Positive Impact through Investments in Innovators
Since our establishment in 2018, The Mills Fabrica's venture fund has been at the forefront of investing in and empowering revolutionary technologies. These cutting-edge innovations can potentially preserve our planet's balance and strengthen our social-ecological resilience. We have identified the following key categories where these transformative technologies can make a significant impact:
- Accelerating Circularity: Driving circularity in the supply chain to optimize the use of resources and reduce reliance on virgin materials.
- Development of Novel Material, Processes, and Manufacturing Systems: Accelerating next-gen material innovation and biological and garment manufacturing that’s more energy and resource efficient and less polluting.
- Advancing Alternative Ingredients: Changing how food is produced by using natural processes that reduce pressure on natural resources and better safety profile of food for better health and well-being.
- Promoting Conscious Consumption: Leveraging technology to create sustainable platforms and brands that enable a conscious lifestyle and to transfer sustainability knowledge to consumers to bring about behavioral change over time.
Part 4: Impact Realized – How our Portfolio Companies are Making Planet-Positive Impact
Impact Realized
Each of our portfolio company is generating at least one type of positive impact — harmonized with the planetary boundaries — intrinsic to their business model.
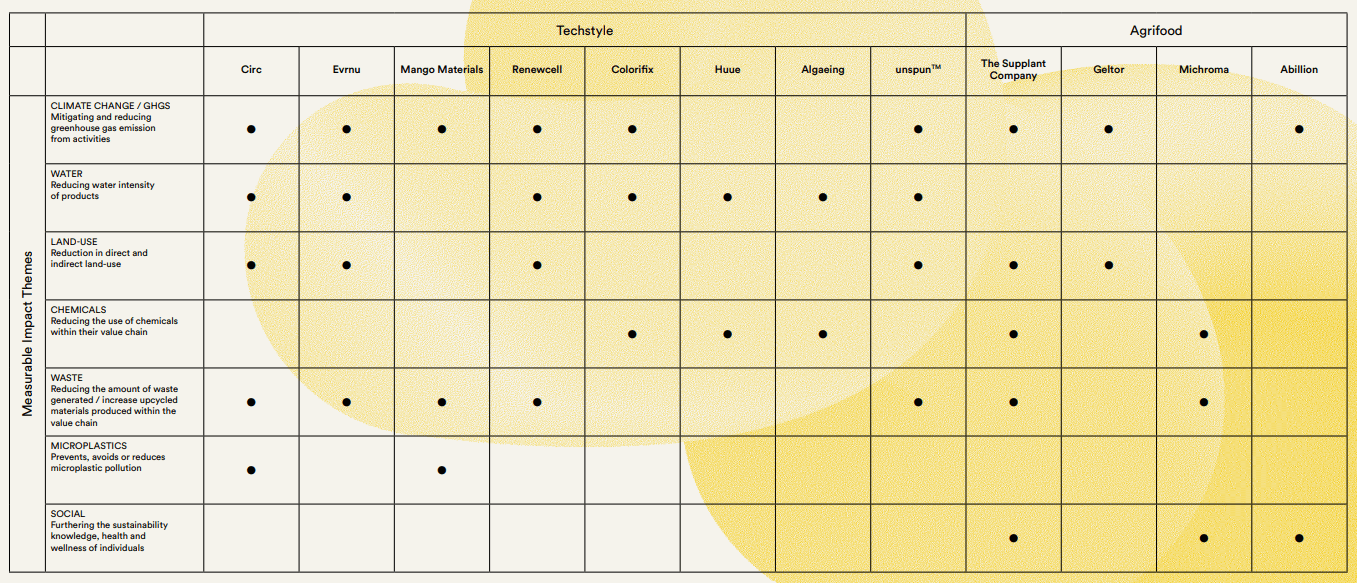
Part 5: Portfolio Highlights
Given the breadth and depth of our ecological issues, as exemplified by the planetary boundaries, The Mills Fabrica has always believed in investing across the entire value chain of both the textile and apparel, and agrifood industry, in order to generate planet-positive impact.
We are highlighting the following from our portfolio:
Textile and apparel industry:
- Circ: material and yarn production
- Colorifix: wet processes and fabric preparation
- unspun™: brand operation, garment production
Agrifood industry:
- abillion: retail and knowledge platform
- The Supplant Company: recycling agricultural side-streams
- Bits x Bites : a food tech VC fund that invests in early-stage startups with transformative technologies to address the most critical challenges in the food system in Mainland China